1. Introduction
As decentralized finance (DeFi) grows, a thorough DeFi audit by a reliable economic auditor has never been more critical. Protocols today manage millions (often billions), making them prime targets for DeFi exploits and sustainability challenges. Despite the growing importance of these audits, they remain a rare occurrence in the ecosystem, underscoring the need for a trusted DeFi auditing company.
While smart contract security audits have become an industry standard, ensuring the economic integrity of a protocol is just as vital for its long-term success. Economic audits are expected to follow the trajectory of smart contract security audits, evolving into a standard practice to safeguard DeFi protocols and ensure their financial resilience.
Without proper web3 audits, protocols risk vulnerabilities like incentive misalignment, unsustainable tokenomics, and systems prone to market manipulation. Addressing these risks requires a specialized approach, blending financial modeling, mechanism design, and blockchain analytics.
We’ll explore the essential role of DeFi economic audits, explaining what they involve, why they’re indispensable, and how to choose the right auditor to secure your protocol’s financial future. Whether you're launching a new protocol or optimizing an existing one, this article will provide the insights you need to strengthen your project's economic foundation and position it for sustainable growth.
2. What Are DeFi Economic Audits?

A DeFi audit is an economic review of a protocol’s incentives, parameters, and market behavior. It stress-tests tokenomics, liquidation logic, oracle dependencies, and game-theoretic design to reduce DeFi exploit risk and improve sustainability. It complements, rather than replaces, smart-contract code audits. If you’re building on Aptos or Sui, consider a Move audit to assess Move-based smart contracts.
What it covers
- Tokenomics & sustainability: Emission schedules, distribution, and incentive alignment to prevent inflationary or mercenary-capital dynamics.
- Mechanism design & parameterization: Collateral factors, liquidation thresholds, interest-rate models, and fee/reward loops tuned for stability and growth.
- Risk modeling & stress tests: Oracle drift, network bottlenecks, black-swan scenarios, and parameter stress-testing across historical and simulated markets.
Outcomes
- Calibrated parameters with decision-ready recommendations.
- Reduced exploit surface area and clearer risk disclosures for stakeholders.
- Sustainable growth levers that improve capital efficiency and user retention.
2.1. Core Focus Areas of Economic Audits

Mechanism Design and Parameterization
At the heart of every DeFi protocol lies its mechanism design, the rules and parameters that govern and determine how it works.
Let’s take money markets as an example. This includes critical factors such as collateralization ratios, liquidation thresholds, interest rate models, and incentive structures for borrowers and lenders. Economic audits assess whether these parameters are appropriately calibrated to maintain stability and promote optimal behavior across all kinds of different actors.
For example, improperly listed assets with inadequate liquidation and risk parameters can result in catastrophic scenarios like what occurred with Mango Markets. In this case, a low-liquidity, long-tail asset was used as collateral to borrow large quantities of fat-tail assets. When the price of the long-tail asset crashed, the protocol was left absorbing bad debt, as the value of the borrowed assets far exceeded the value of the collateral. This highlights the importance of not only evaluating parameters like collateral factors and liquidation incentives but also incorporating stress tests and scenario analysis for edge cases.

By evaluating these parameters, auditors help protocols achieve an equilibrium where user incentives align with the protocol’s long-term goals, fostering both stability and growth.
Risk Modeling
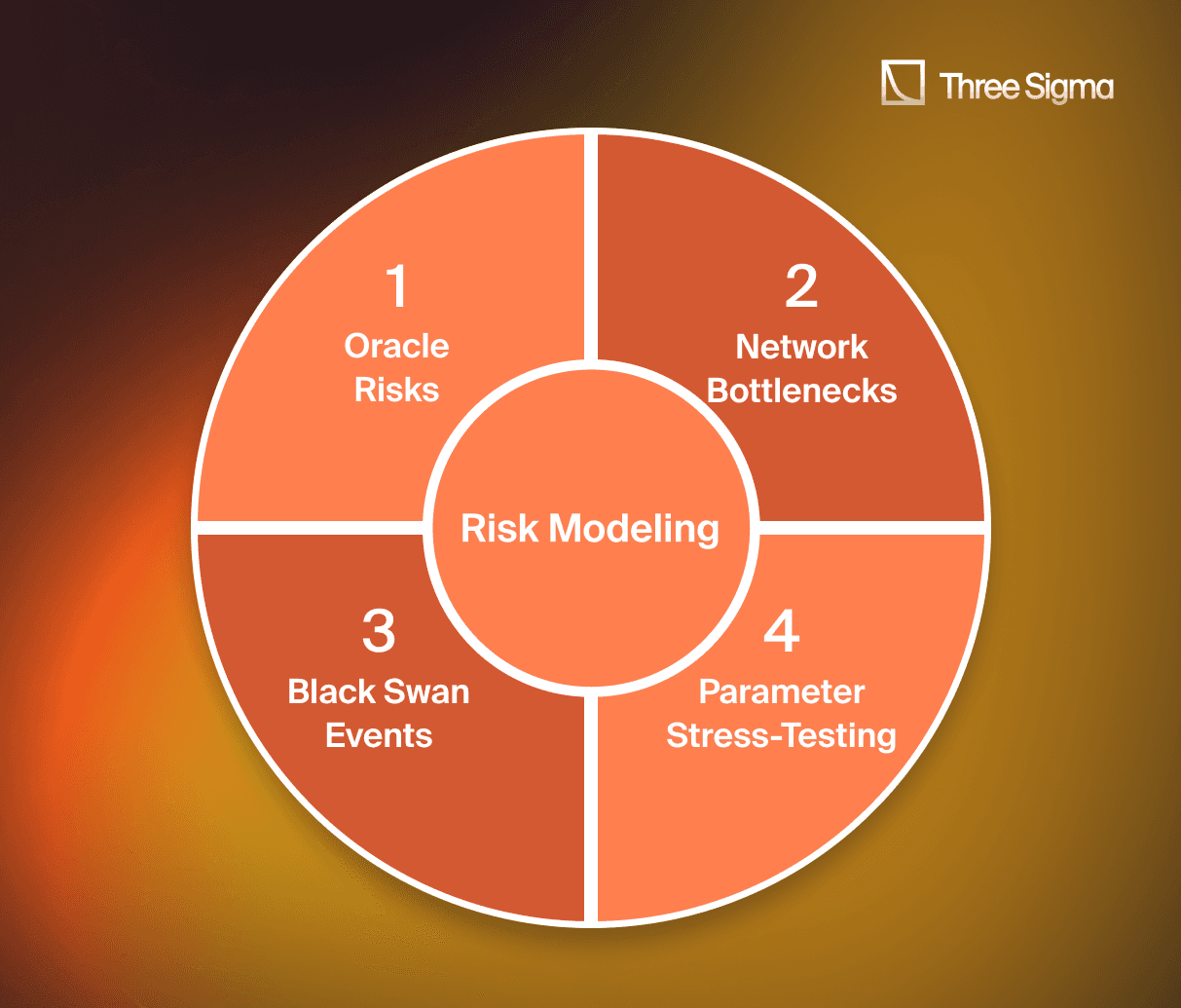
Economic audits involve rigorous risk modeling to identify potential vulnerabilities arising from market dynamics. Our models surface potential DeFi exploit patterns (e.g., oracle drift) and quantify how a DeFi audit can harden parameters.
This includes assessing systemic risks such as:
- Oracle risks: Assessing the impact of stale or delayed price feeds on liquidation events and designing strategies to minimize reliance on a single oracle provider.
- Network bottlenecks: Evaluating how high gas fees and slow block confirmations (e.g., on high-demand L1s or congested L2s) affect liquidation efficiency and overall protocol stability.
- Parameter stress-testing: Using tools like Monte Carlo or Cox-Ingersoll-Ross (CIR) models to test liquidation thresholds and collateral volatility against real-world price deviations and historical market conditions.
- Black swan events: Modeling catastrophic scenarios, such as market crashes or stablecoin de-pegging, to determine the protocol’s resilience and develop mitigation strategies, such as insurance funds or enhanced stability mechanisms.
By employing these methodologies, auditors can provide actionable insights to optimize a protocol’s parameterization, ensuring it remains robust even under the most challenging circumstances.
How a DeFi audit mitigates common DeFi exploits
- Oracle manipulation: verify multiple sources, use medianization and stale-feed guards to reduce reliance on a single oracle.
- Liquidation cascades: stress-test slippage, network delays, and keeper incentives to ensure stability during market downturns.
- Market manipulation loops: identify reflexive fee/reward structures and flash-loan vectors that create hidden feedback risks.
- Peg and discount attacks: model stablecoin and LST exposures under de-peg scenarios and assess cross-collateral contagion.
Sustainability and Tokenomics Optimization
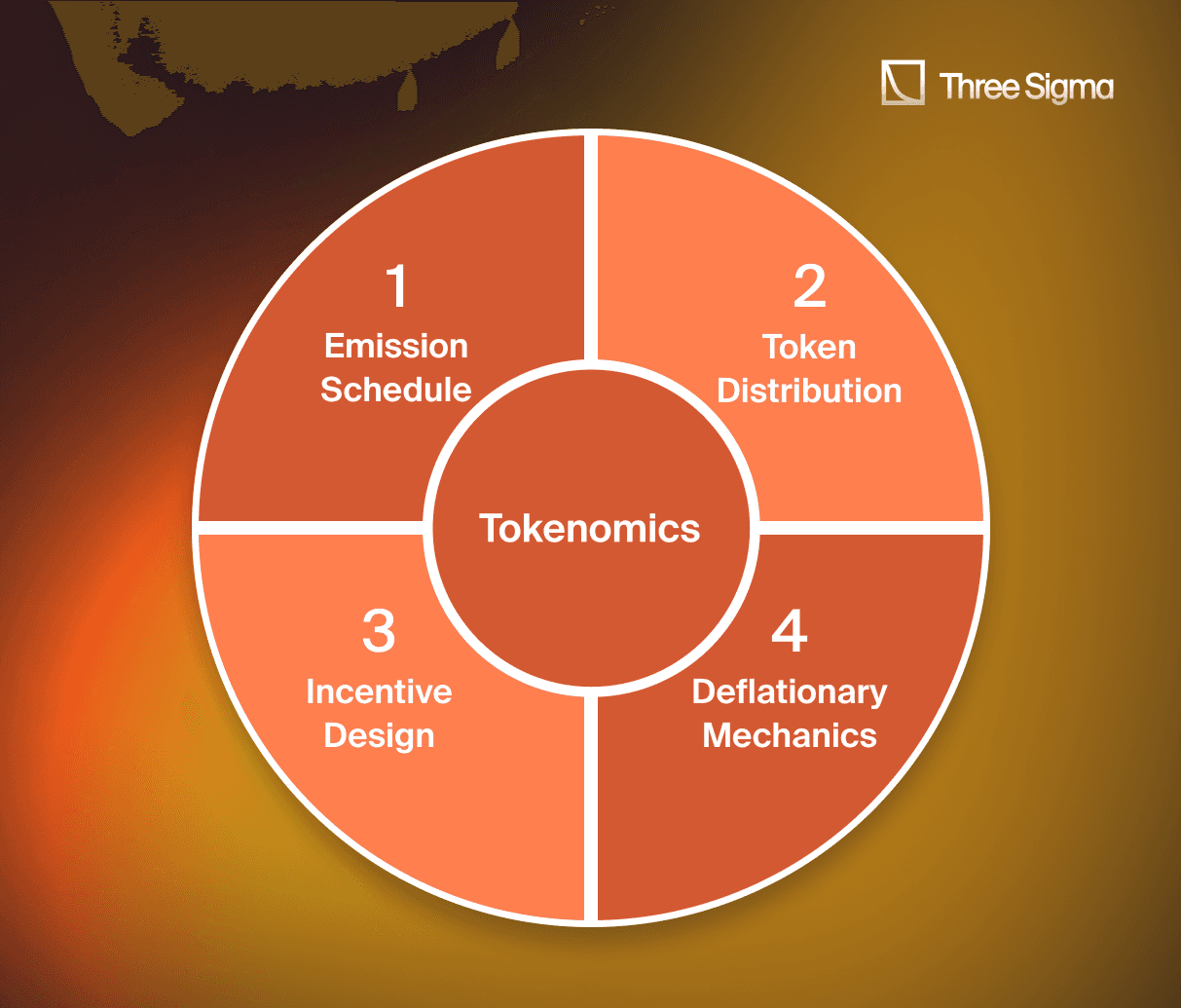
A protocol’s success hinges on sustainable tokenomics. Economic audits refine emission schedules, token distribution, and incentives to balance liquidity, user engagement, and growth.
- Emission Schedules: Tail emissions and decay models control inflation while maintaining liquidity incentives. Simulations test sustainability under varying conditions.
- Token Distribution: Equitable distribution avoids governance dominance and sudden sell-offs. Vesting schedules ensure stability and align stakeholder interests.
- Incentive Design: Rewards must drive participation without encouraging short-term behaviors. Comparative analysis ensures alignment with protocol goals.
- Deflationary Mechanics: Strategies like token burns or fee redistributions create buy pressure and enhance value. Adaptive fees balance incentives for liquidity providers and governance participants.
Optimized tokenomics foster long-term resilience and position protocols for competitive success.
2.2. How Economic Audits Differ from Smart Contract Audits

Economic audits and smart contract audits serve complementary but fundamentally different purposes in safeguarding DeFi protocols. A smart contract audit (such as a Solidity or Rust Smart Contract Audit) focuses on technical correctness and security, identifying vulnerabilities such as reentrancy attacks, overflow errors, or unauthorized access risks. It ensures that the code operates as intended and is free from exploitable bugs.
In contrast, an economic audit evaluates the financial systems and incentive structures that underpin a protocol. While a perfectly coded protocol can function flawlessly, it may still fail if its economic design is poorly conceived.
Key differences include:
- Scope: Smart contract audits focus on code-level vulnerabilities, while economic audits examine systemic risks and financial sustainability, yet there’s no standard scope and it varies from audit to audit.
- Methodology: Smart contract audits rely on static code analysis, fuzz testing, and formal verification. Economic audits utilize backtesting, scenario analysis, and stress testing to model real-world behaviors.
- Objective: Smart contract audits ensure secure and functional code. Economic audits ensure the protocol can sustain itself financially and resist manipulation under diverse market conditions.
Together, smart contract and economic audits provide a comprehensive approach to protocol resilience, addressing both the technical and economic foundations necessary for sustainable growth.
3. Why Are Economic Audits Critical?
A DeFi audit evaluates parameters and incentives that can lead to DeFi exploits, complementing code reviews with market-aware analysis. Therefore, economic audits are indispensable for ensuring the long-term stability and resilience of DeFi protocols. As the industry grows, protocols manage billions in assets and face increasingly sophisticated threats. A robust economic audit helps mitigate these risks by stress-testing financial systems and ensuring their sustainability.
An economic audit addresses critical questions such as:

- Are collateralization ratios and liquidation mechanisms resilient to market volatility?
- Do tokenomics create sustainable incentives for participants?
- Are liquidity incentives structured to prevent mercenary capital from draining rewards and destabilizing the protocol?
- Can oracle dependencies handle extreme market volatility without causing mispriced liquidations or systemic failure?
- Do fee and reward mechanisms encourage long-term user engagement rather than short-term speculative behavior?
Economic audits go beyond surface-level security, addressing the financial and systemic risks that can threaten even technically sound protocols. By ensuring stability, sustainability, and user confidence, these audits are crucial for the continued evolution and success of DeFi.
4. Types of Services Offered in DeFi Economic Audits
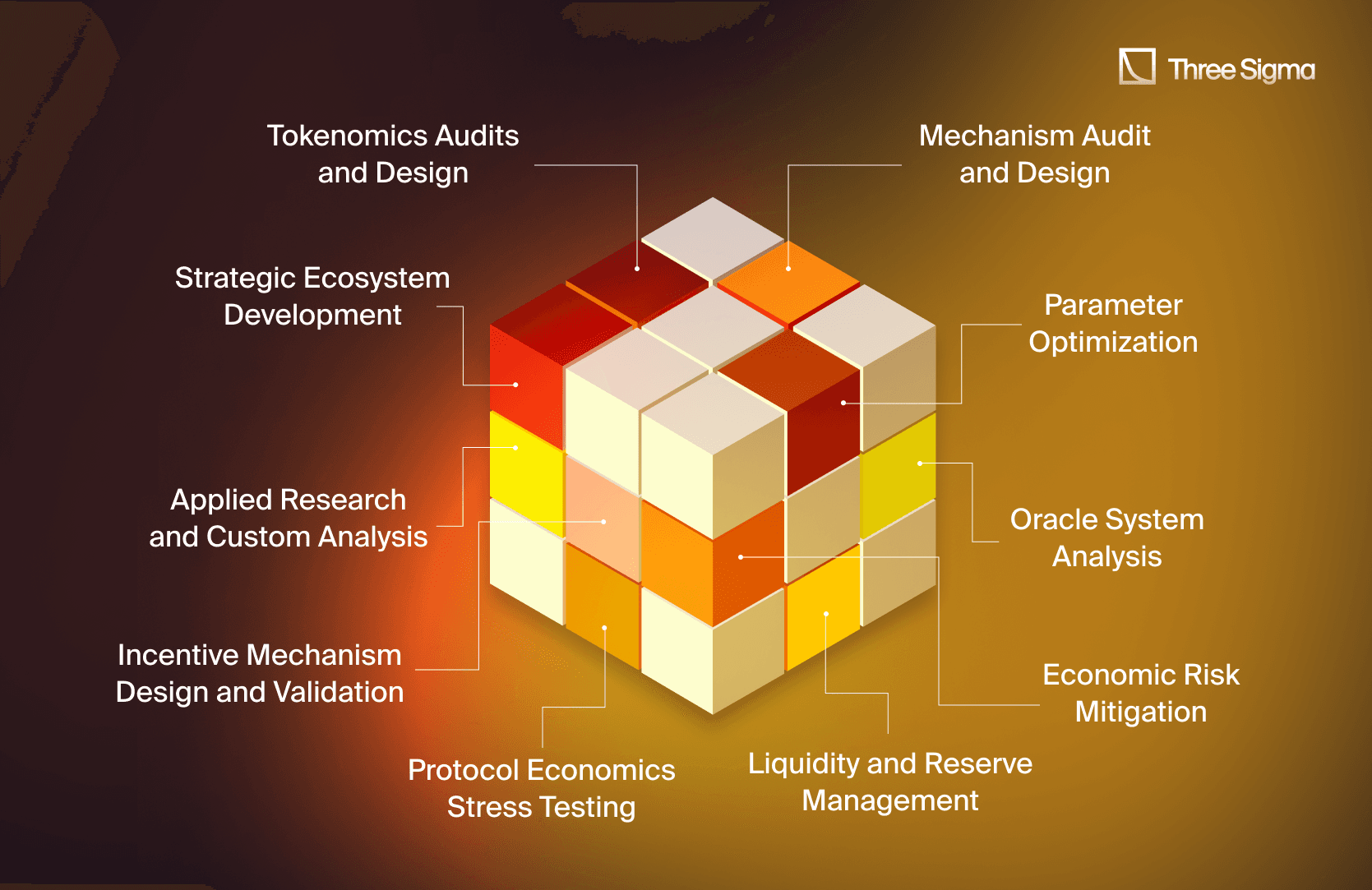
- Designing token supply mechanisms, vesting schedules, and inflation controls.
- Validating existing tokenomics for sustainability and alignment with protocol goals.
- A DeFi audit translates findings into parameterizable changes that reduce DeFi exploit exposure.
Incentive Mechanism Design and Validation
- Developing fair reward structures for liquidity providers and stakers.
- Validating existing incentives to prevent exploitation or misaligned behaviors.
- Creating robust protocol mechanisms for governance, rewards, and market operations.
- Auditing mechanism implementation for alignment with stated economic objectives.
Protocol Economics Stress Testing
- Simulating market conditions to test protocol resilience to events like price crashes or liquidity shocks.
- Providing actionable insights for improving protocol robustness.
Oracle System Analysis
- Ensuring oracle data accuracy and resilience to manipulation or staleness.
- Reviewing dependency risks on off-chain data sources.
Liquidity and Reserve Management
- Designing and validating mechanisms for managing stablecoin reserves and treasury assets.
- Assessing liquidity risks and insolvency scenarios.
- Designing strategies to minimize impermanent loss, slippage, and cascading liquidations.
- Testing proposed mitigation mechanisms under simulated scenarios.
Parameter Optimization
- Precisely calibrating protocol parameters, including interest rates, collateralization ratios, and fee structures, to align with the protocol’s objectives.
- Optimization tailored to specific goals such as maximizing user adoption, enhancing liquidity provider (LP) returns, improving system resilience, or balancing revenue with market risk exposure.
Applied Research and Custom Analysis
- Conducting in-depth research on tokenomics, market trends, and protocol economics.
- Delivering tailored solutions to unique protocol challenges.
Strategic Ecosystem Development
- Conducting in-depth research to identify key priorities for Layer-1, Layer-2, or Layer-3 ecosystems aiming to deploy or expand DeFi applications.
- Evaluating potential protocol deployments and their differentiation from existing forks to build a unique and competitive offering.
- Providing actionable insights and recommendations tailored to the ecosystem’s strengths, market position, and long-term sustainability goals.
5. What to Look for in a DeFi Economic Auditor
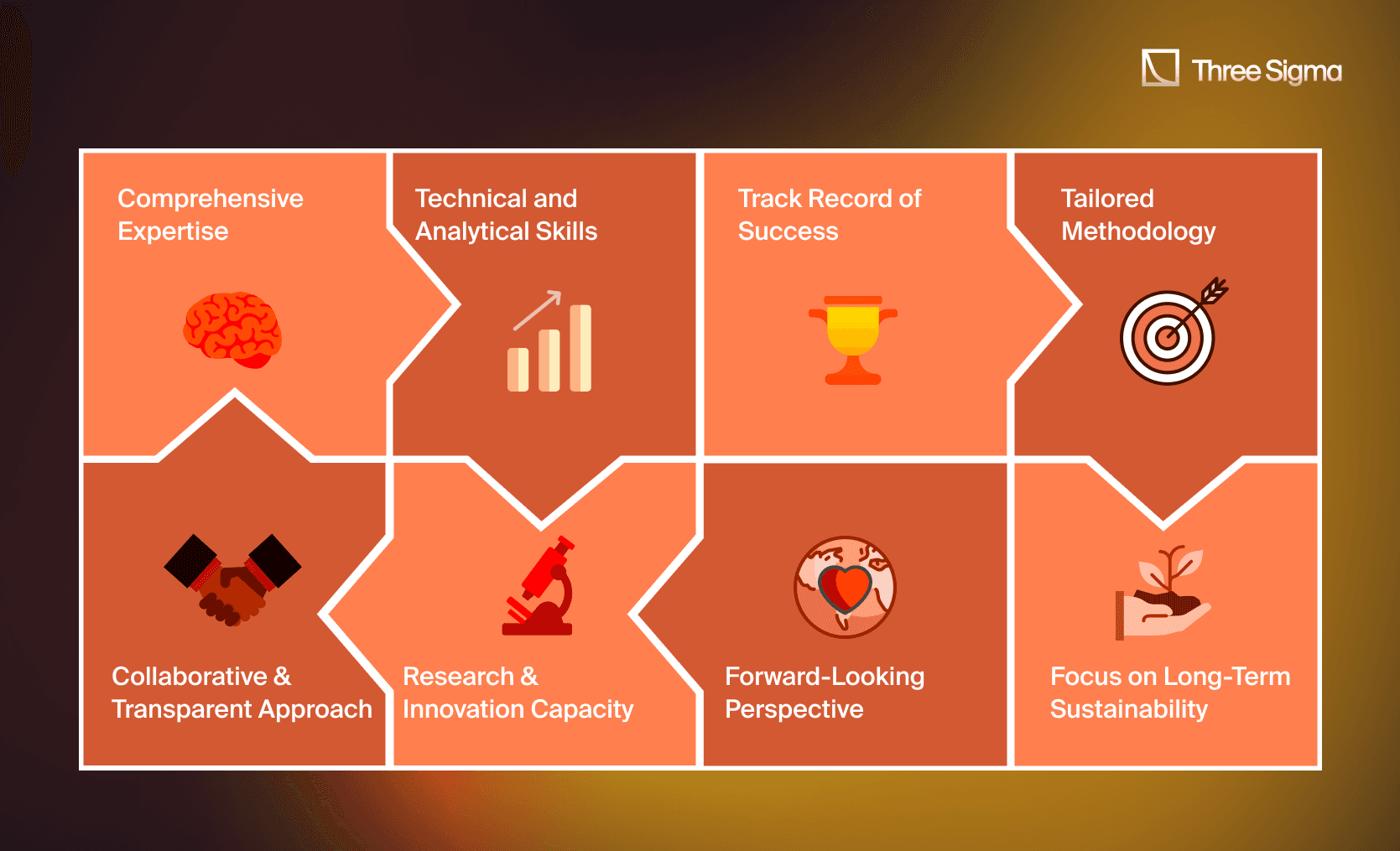
Choosing the right DeFi economic auditor is critical to ensuring your protocol’s long-term stability and growth. Here are the key qualities to prioritize when selecting an auditor:
1. Comprehensive Expertise An exceptional auditor combines a deep knowledge of DeFi protocols, tokenomics, mechanism design, and financial modeling. Look for teams that understand the nuances of governance systems, incentive structures, and risk mitigation. Experience with leading protocols like Aave, Uniswap, or GMX signals familiarity with complex ecosystems and high-stakes environments.
2.Technical and Analytical Skills Effective auditors possess a blend of blockchain-specific skills and data-driven expertise:
- Blockchain Proficiency: Ability to read smart contracts, analyze on-chain transactions, perform **Solidity audits** and assess vulnerabilities within governance and incentive mechanisms.
- Data Analytics: Proficiency in Python, SQL, and advanced simulation frameworks to extract, model, and interpret complex datasets.
- Simulation and Stress Testing: Expertise in using tools for agent-based modeling, scenario testing, and Monte Carlo simulations to evaluate protocol behavior under various market conditions.
3. Track Record of Success: Proven experience in conducting economic audits, mechanism design, and parameter optimization is a must. Review their portfolio for impactful results, such as improved protocol efficiency, mitigated risk scenarios, and enhanced capital utilization. Case studies, published reports, or references from previous clients can validate their expertise.
4. Tailored Methodology: Each protocol is unique, and so is each audit. The auditor should adapt their approach based on your specific needs, such as tokenomics design, liquidation mechanism validation, or cross-protocol interaction modeling. A one-size-fits-all strategy often misses critical nuances in your protocol’s ecosystem.
5. Collaborative and Transparent Approach: Auditors must work closely with your team, fostering open communication and collaboration throughout the engagement. Regular updates, detailed reports, and actionable insights are vital for integrating findings effectively into your protocol. Auditors who can seamlessly partner with developers, governance teams, and stakeholders add immense value.
6. Research and Innovation Capacity: Look for auditors who actively contribute to the DeFi ecosystem through research. Teams that publish articles, develop new modeling tools, or analyze emerging trends signal their commitment to advancing economic security and their ability to stay ahead of industry changes.
7. Forward-Looking Perspective: Beyond assessing current risks, a great auditor anticipates future challenges. This includes modeling for black swan events, preparing for evolving regulatory environments, and ensuring the protocol’s mechanisms remain robust as DeFi markets mature.
8. Focus on Long-Term Sustainability: The auditor should prioritize recommendations that align with your protocol’s long-term objectives. Whether optimizing token emissions, refining incentive structures, or designing deflationary mechanisms, their insights should promote durability and scalability.
By selecting an auditor with these attributes, you can secure not only your protocol’s immediate safety but also its ongoing relevance and competitiveness in the dynamic DeFi ecosystem.
DeFi audit deliverables & timeline
- Deliverables: risk report, parameter recommendations, tokenomics tuning, scenario models, governance proposals.
- Timeline: discovery → modeling → review → final report + presentation.
- Outcome: measurable reductions in attack surface and insolvency risk.
Why Choose Three Sigma?

At Three Sigma, we combine expertise and research to deliver economic audits that improve resilience and growth. To discuss scope or availability, **book a DeFi audit.** Whether it’s optimizing tokenomics, designing incentive mechanisms, or conducting comprehensive stress tests, we help protocols achieve resilience, sustainability, and long-term growth.
Broad Experience Across DeFi Verticals
Our work spans a wide array of DeFi applications, from lending and borrowing protocols to governance systems, liquidity pools, and perpetual markets. This diversity gives us the unique ability to understand and enhance complex ecosystems.
Proven Impact
Our audits and recommendations have driven measurable improvements, including enhanced capital efficiency, reduced risk exposure, and optimized protocol designs. Our clients consistently achieve greater market competitiveness and improved user confidence.
Research-Driven
Beyond audits, we’re committed to advancing DeFi through research. From exploring volatility metrics in crypto markets to analyzing tokenomics frameworks, our insights help shape the future of the ecosystem.
Expert Team
Led by experienced professionals with backgrounds in mathematics, engineering, and blockchain technology, our team combines deep technical knowledge with a hands-on, collaborative approach to deliver results that matter.

Fuel Network
Fuel Network — Blocktime Optimization
Conducted research into methods for optimizing block finality in the Fuel Network. Our focus was on reducing block finality times to improve transaction throughput and network responsiveness. Shorter block finality is beneficial for faster confirmation times, while longer block finality can hinder transaction finality speed.

Uniswap Foundation
Uniswap Foundation — ERC-7683 Impact
In our governance-focused research for Uniswap, we examined the potential impact of ERC-7683 on intent-based protocols and on-chain liquidity dynamics. Our findings shared through this governance post, have informed strategies for adapting Uniswap’s liquidity framework in light of this evolving standard.

Filecoin Incentive Design Labs (FIDL)
Filecoin Incentive Design Labs (FIDL) - Incentive Design
We assessed the economic impact of the FIL+ program on block rewards. This engagement offered a comprehensive understanding of how the Fil+ mechanism influences Filecoin's economic health, especially in scenarios where the program evolves or phases out. Our work focused on identifying and prioritizing key areas, such as the relationship between block rewards and the storage incentives driven by Fil+.
Choosing the right auditor can make or break protocol trust, especially when economic design is the product. Our DeFi Ecosystem Strategic RD service helps you evaluate your assumptions, token dynamics and incentive models with the depth they deserve.
FAQ
- Do I need a DeFi audit if I already did a code audit?
Yes. A code audit checks smart-contract correctness; a DeFi audit evaluates incentives, parameters, tokenomics, oracles, and market behavior. Many failures stem from design economics (not code). The two audits are complementary and together reduce DeFi exploit risk and insolvency scenarios.
- What does a DeFi audit include?
Scope typically covers tokenomics and emissions, mechanism design and parameterization (LTVs, liquidation thresholds, fee/reward loops), oracle and market-structure risks, stress tests and scenario modeling, liquidity/treasury analysis, and governance/economic attack surfaces, ending with prioritized, actionable recommendations.
- How does a DeFi audit prevent DeFi exploits?
By modeling likely attack paths and calibrating defenses: oracle medianization and stale-feed guards, sane LTVs and liquidation incentives, circuit breakers and caps, anti-manipulation fees, keeper/rebalancing design, and stress-tested parameters. The result is fewer profitable vectors and earlier detection of cascading-liquidation risks.
Conclusion
A rigorous DeFi audit turns insights into guardrails, shrinking DeFi exploit surface area and strengthening long-term sustainability. Economic audits are essential for the stability and sustainability of DeFi protocols. By evaluating tokenomics, incentive structures, and systemic risks, these audits go beyond technical security to ensure a protocol’s financial resilience. They address critical vulnerabilities such as misaligned incentives, unsustainable tokenomics, and susceptibility to market manipulation, providing actionable insights to optimize mechanisms and foster long-term growth.
Choosing the right auditor is equally important. Look for auditors with a strong track record, deep expertise in financial modeling and mechanism design, and a collaborative approach tailored to your protocol’s unique challenges. A robust economic audit safeguards against risks and positions your protocol for success in the competitive DeFi landscape.
Ready to leverage your DeFi Protocol?
Secure your protocol’s future with an economic audit that ensures resilience, sustainability, and growth. Don’t just survive DeFi, thrive in it.

Economic Security Lead
Pablo holds a Master's in management, having focused in finance, and with a thesis on DeFi, demonstrating his knowledge and expertise in this field. He has extensive experience in research and analysis of DeFi protocols, having worked as an analyst at Siemens and a DeFi researcher at Deep Tech Ventures. His background in finance, research and analysis skills are a valuable addition to our team.